01
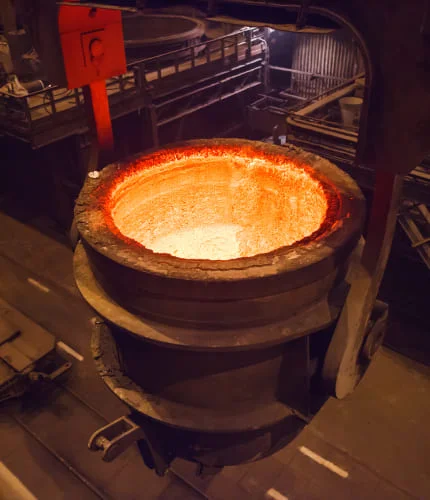
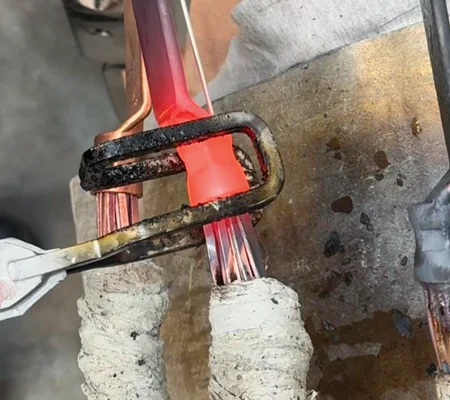
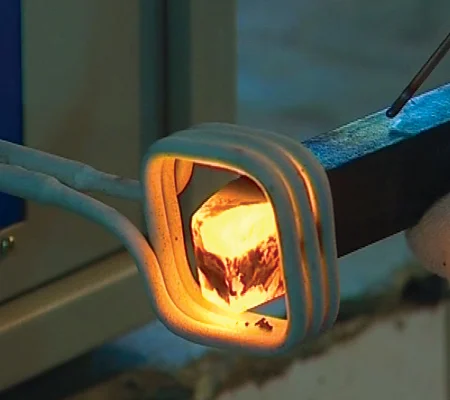
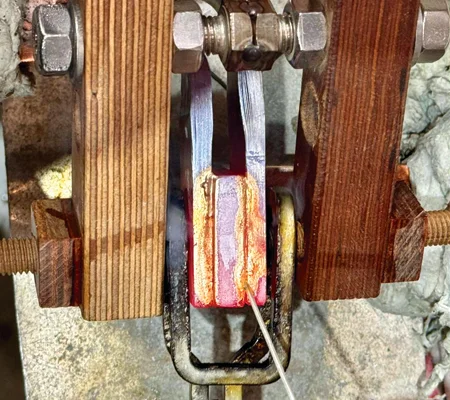
The metal components to be joined are first cleaned and prepped for optimal adhesion. A filler material, usually a metal alloy with a lower melting point, is positioned between the parts to be brazed.
02
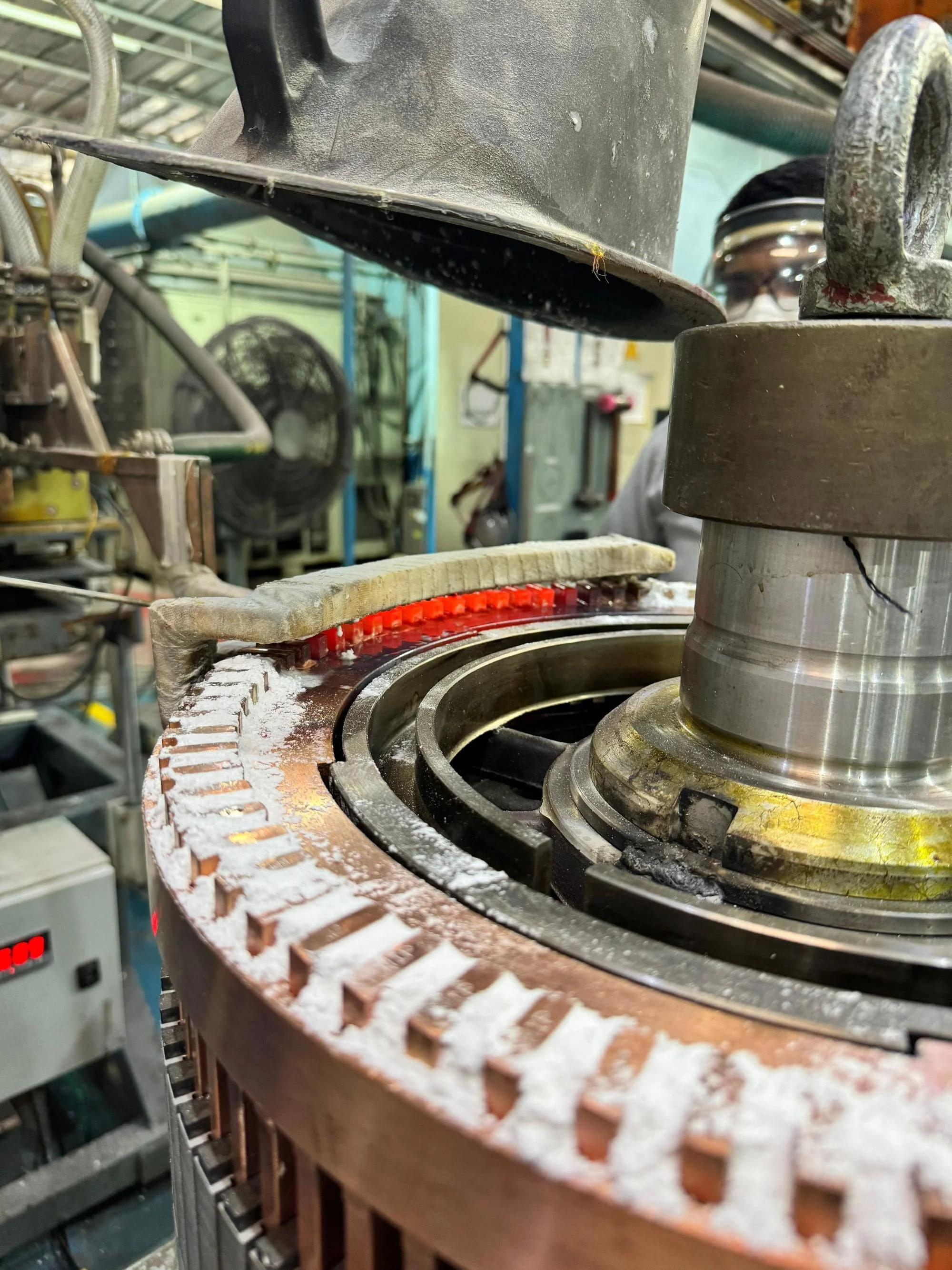
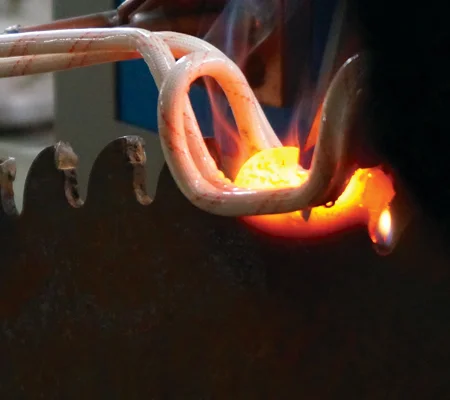
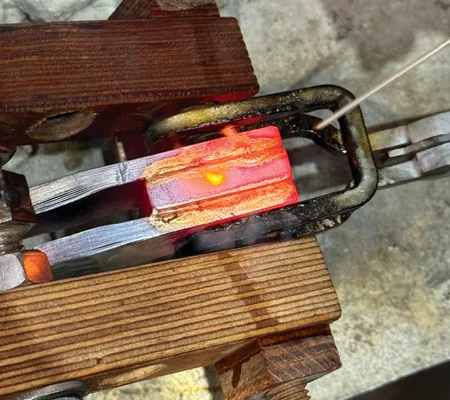
The induction brazing machine employs an induction coil to produce an electromagnetic field, which generates eddy currents in the metal parts, causing them to heat rapidly. This targeted heating ensures that only the joint area reaches the necessary temperature. As the parts heat up, the filler metal melts and is drawn into the joint by capillary action.
03
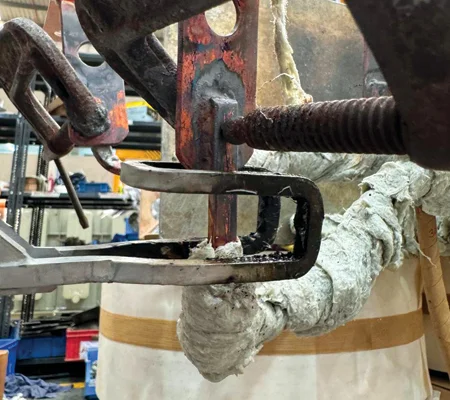
The temperature is precisely controlled to melt the filler metal without overheating the base metals. Once the molten filler metal cools and solidifies, it forms a strong, durable bond between the metal parts.
04
The cooling process can be managed to enhance the properties of the brazed joint. After brazing, the joined parts may undergo further processes such as cleaning, inspection, or heat treatment to improve the joint’s characteristics or appearance.