01
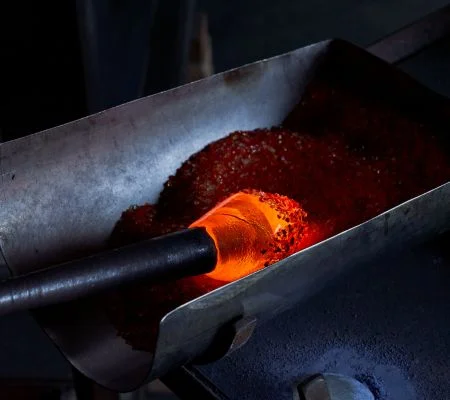
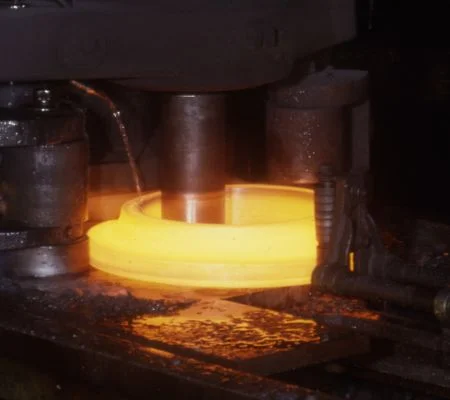
The metal parts to be joined are cleaned to remove contaminants, ensuring a strong bond. The filler material, typically a metal alloy with a lower melting point than the base metals, is positioned at the joint. The induction brazing machine uses an induction coil to generate an electromagnetic field, which induces eddy currents in the metal parts. These eddy currents rapidly heat the metal parts, focusing on the area around the joint to reach the brazing temperature. The localized heating causes the filler material to melt. Capillary action draws the molten filler into the joint, filling the gap between the base metals. Once the filler material has flowed into the joint, the heat is removed, allowing the joint to cool. As the joint cools, the filler material solidifies, creating a strong, durable bond. The brazed components may undergo additional treatments like cleaning, inspection, or heat treatment to optimize the joint's properties or appearance.